-
News & Events

Source: Bioworld

Homo neanderthalensis, a hominin that was active in Europe 200,000 years ago, dominated Europe, Western Asia and northern Africa 120,000 years ago, but surprisingly, around 35,000 years ago, the range of Neanderthals began to shrink rapidly and eventually disappeared completely by about 30,000 years ago.
Remarkably 35,000 years ago, it was the time when Homo sapiens (modern humans) came to Europe. Many scholars believe that it was the arrival of Homo sapiens that brought the catastrophe of the Neanderthals, leading to their total extinction.
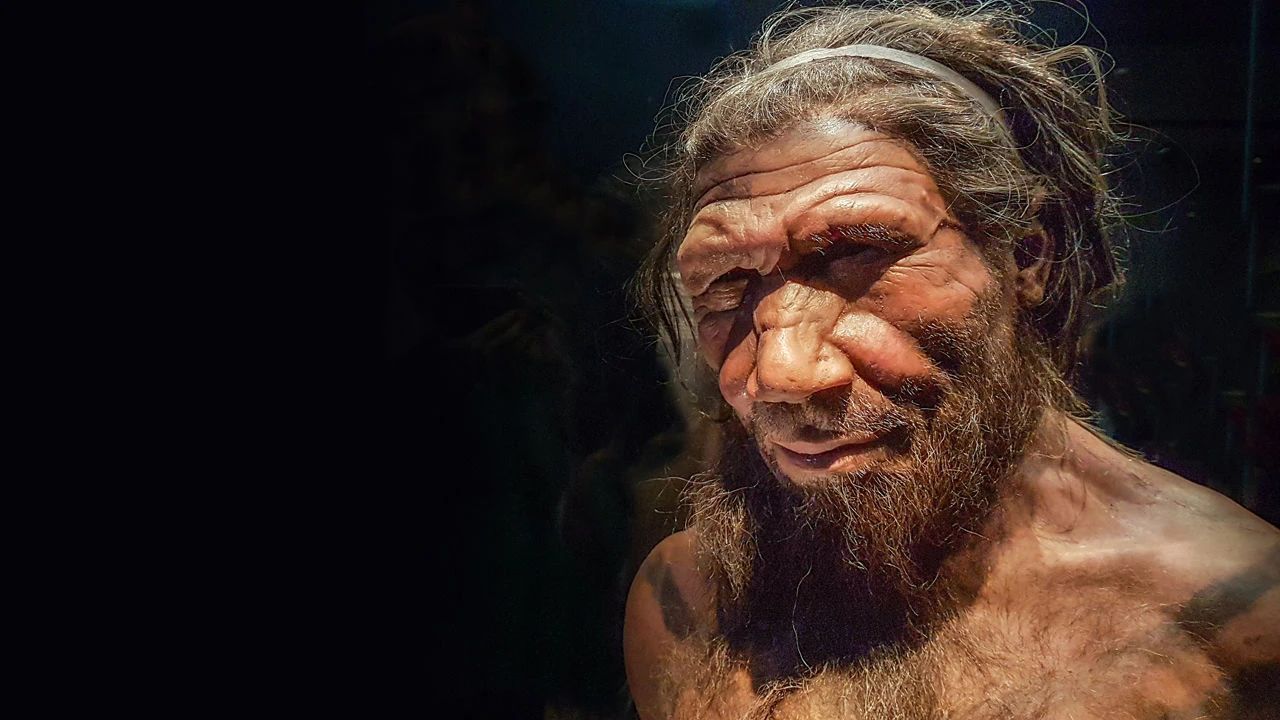

A restored image of the Neanderthal
Neanderthals as a species have been extinct for tens of thousands of years, but they actually still exist to some extent. During the brief period that Homo sapiens and Neanderthals co-existed, the two species interbred, therefore the Neanderthal’s genes remained in Homo sapiens forever. And it could tell from the DNA analysis that modern humans share 1% to 4% of the Neanderthal genetic component.
In fact, some of the characteristics in modern humans are inherited from Neanderthal genes. For example, in July 2020, a research published in the journal Current Biology showed that pain sensitivity in modern humans is linked to Neanderthal traits【1】. Another research from Journal Molecular Biology and Evolution published in June 2020 pointed out that one in three women in Europe inherited the receptor for progesterone from Neanderthals【2】, a gene variant associated with increased fertility, fewer bleedings during early pregnancy and fewer miscarriages. Both researches are from the team of Svante P??bo, the winner of the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
In September 2020, Svante P??bo proposed in his paper that genes from extinct Neanderthals have also been linked to how modern humans' immune systems respond to viral infections.
This research, titled The major genetic risk factor for severe COVID-19 is inherited from Neanderthals, was published in Nature, an international top academic journal.

The vast majority of COVID-19 patients have mild or even asymptomatic symptoms, but severe patients are at greater risk. And the previous study showed that the major genetic risk factor of becoming severely ill with COVID-19 is the gene cluster on chromosome 3.
The study in Nature also confirmed that the risk of severe COVID-19 was caused by a genome fragment of about 50 kb in length inherited from Neanderthals. This genetic risk is highest in populations in South Asia and Europe, but almost none in East Asia and Africa.
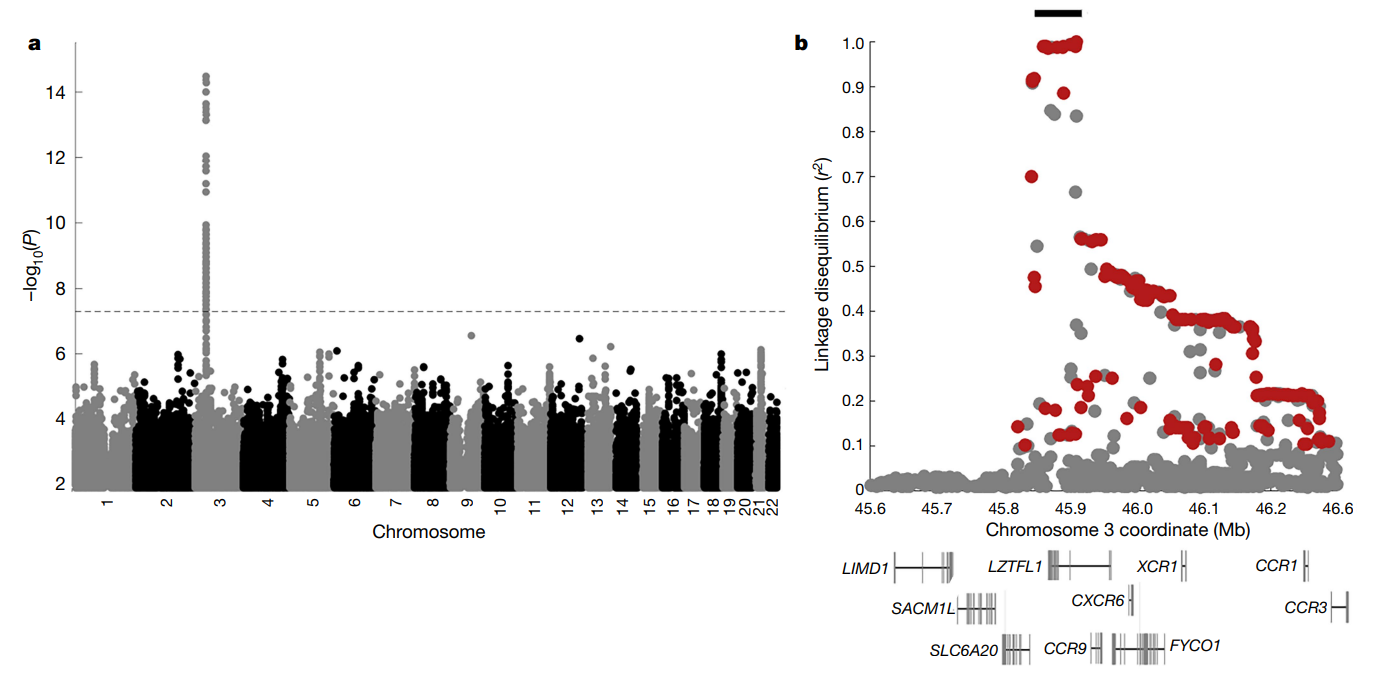
Genetic variants associated with severe COVID-19
Further analysis showed that Neanderthals' core risk gene fragment for severe COVID-19 occurred at 30 percent of the population in South Asia, 8 percent in Europe, an average of 4 percent in the Americas, and almost none in East Asia and Africa.
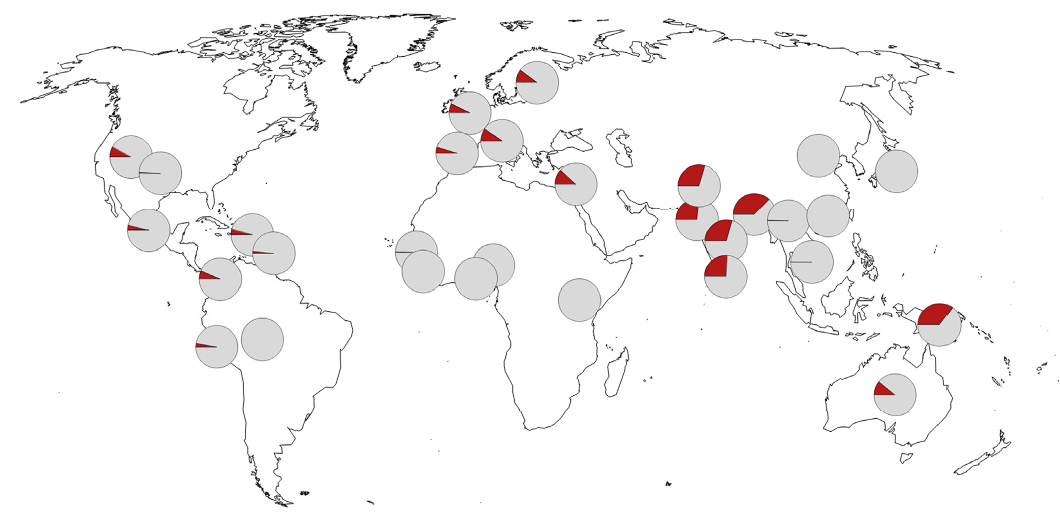
This means that after being infected with COVID-19, the possibility of Chinese people developing severe COVID-19 is low, and indeed so it is.
Reference:
1、https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.06.045
2、https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa119
3、https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-020-2818-3
